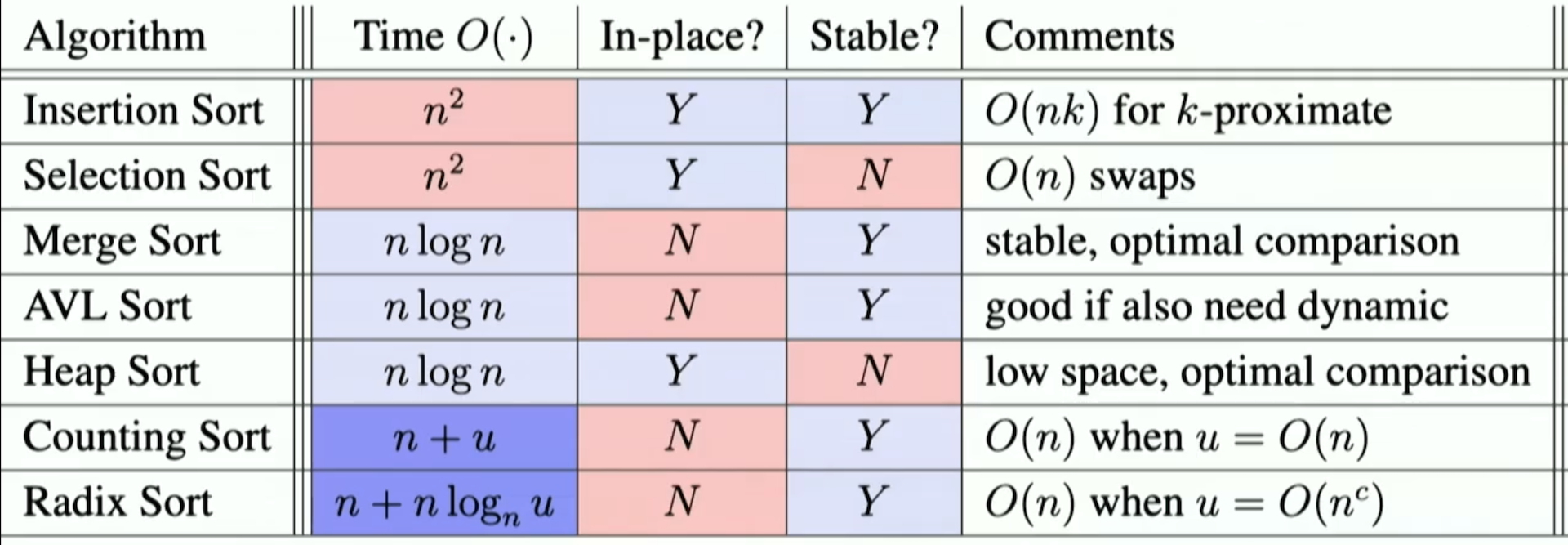
排序算法对比
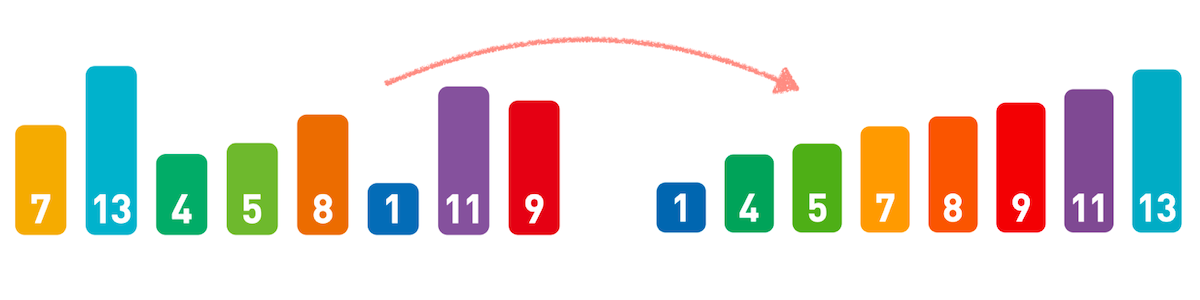
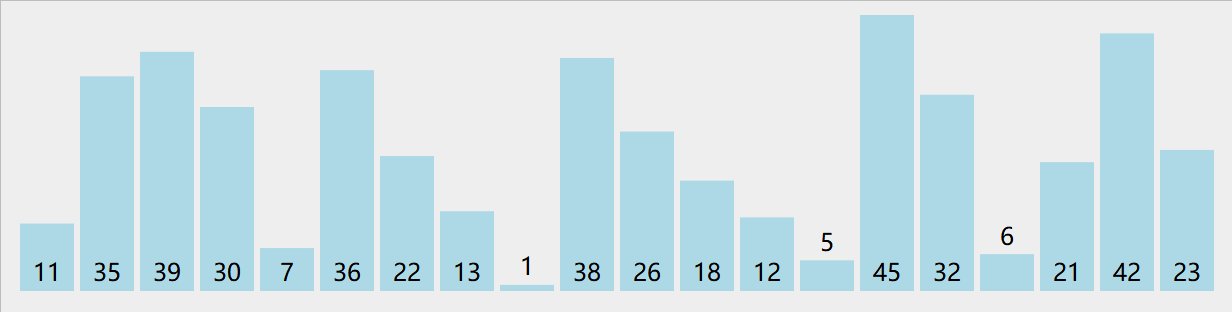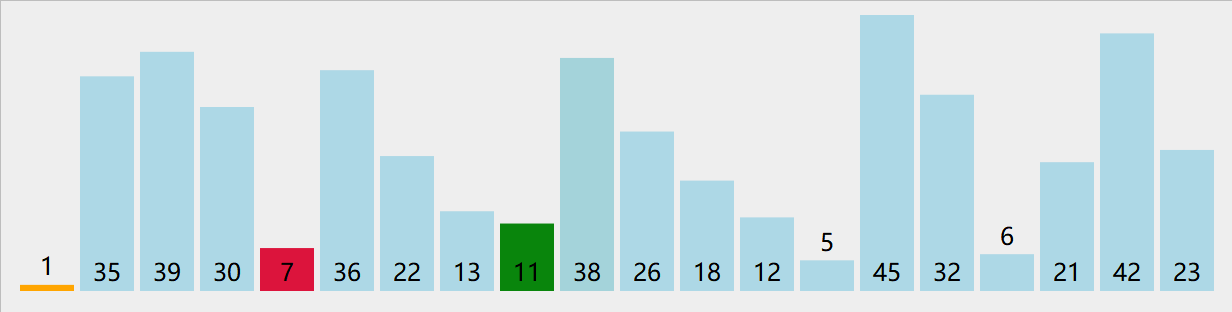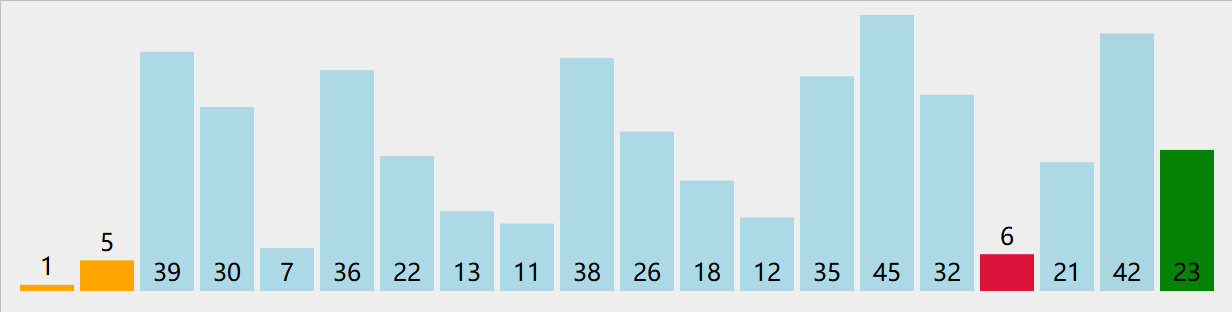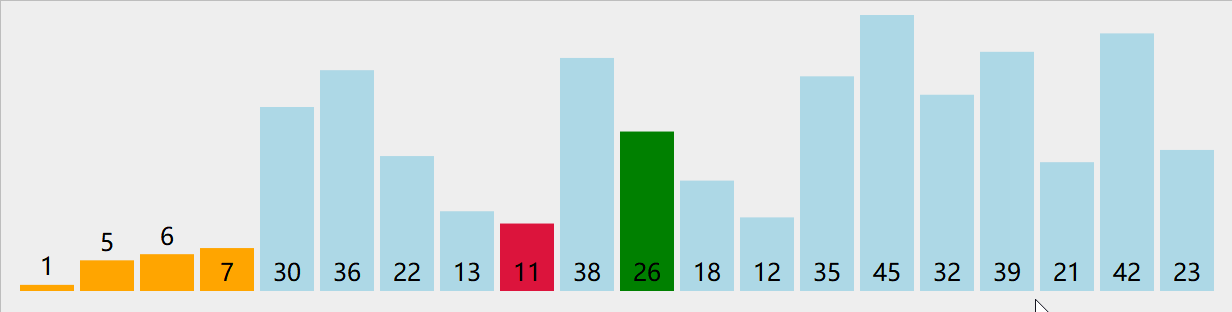
选择排序
- 每次将未排序序列的最大元素放入已排序序列的开头
- in-place算法,时间复杂度O(n^2),排序算法不稳定
1 | def selection_sort(A): |
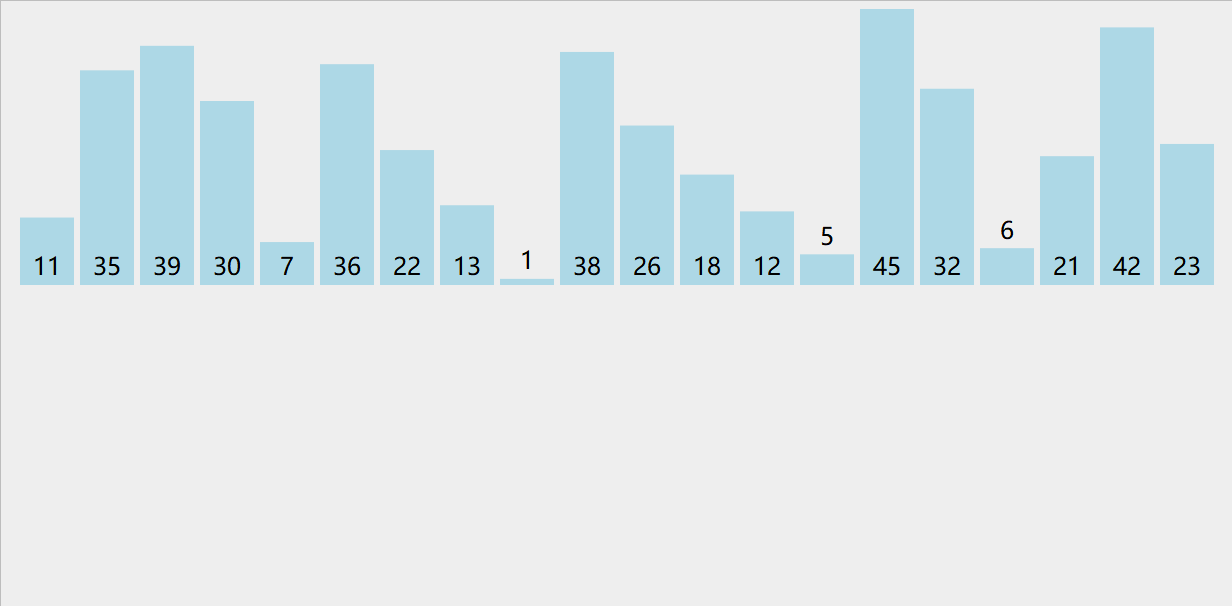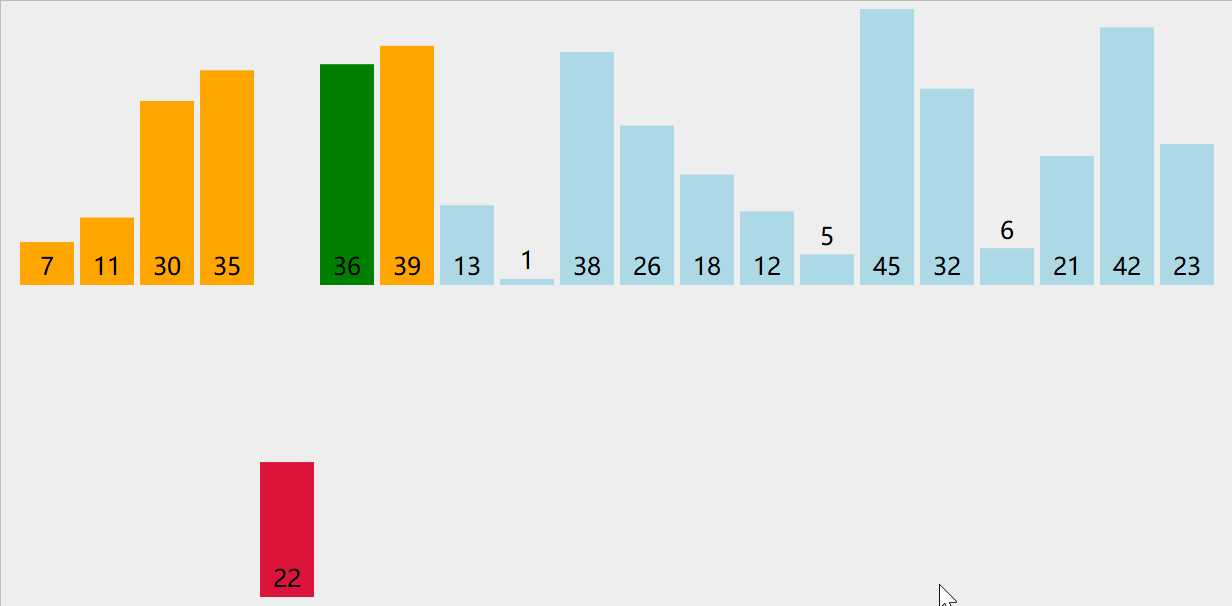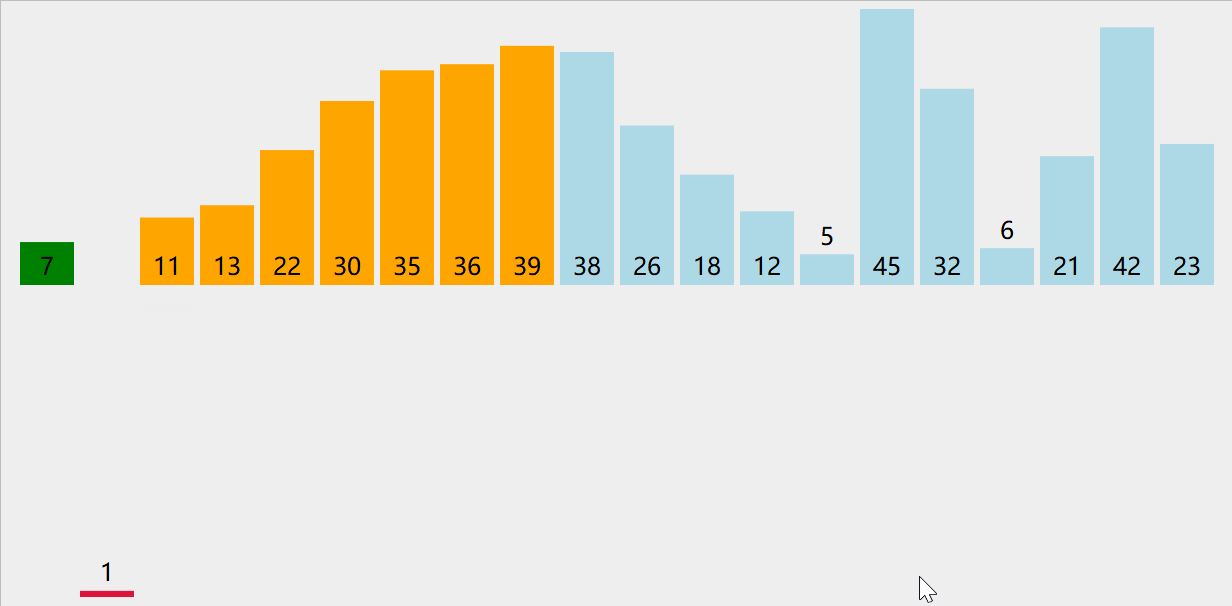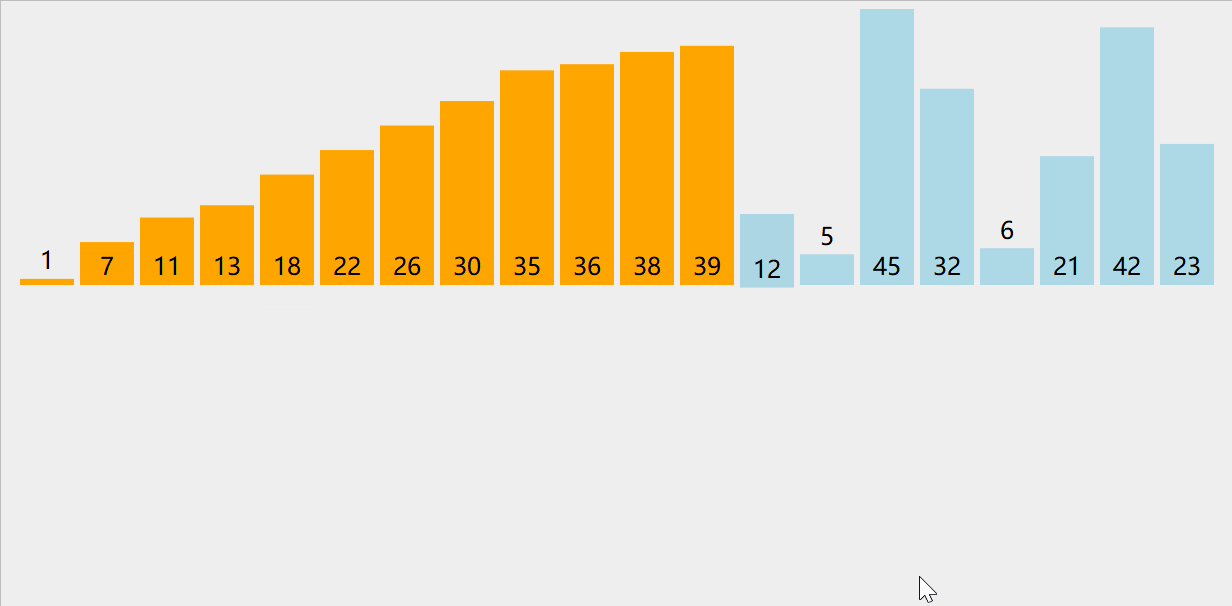
插入排序(Insertion Sort)
- 每次将一个待排序元素插入到已排序序列中的合适位置
- in-place算法,时间复杂度O(n^2),排序算法稳定
1 | def insertion_sort(A): |
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
- 每次交换相邻的两个元素,直至没有需要交换的元素
- in-place算法,时间复杂度O(n^2),排序算法稳定

1 | def bubble_sort(A): |
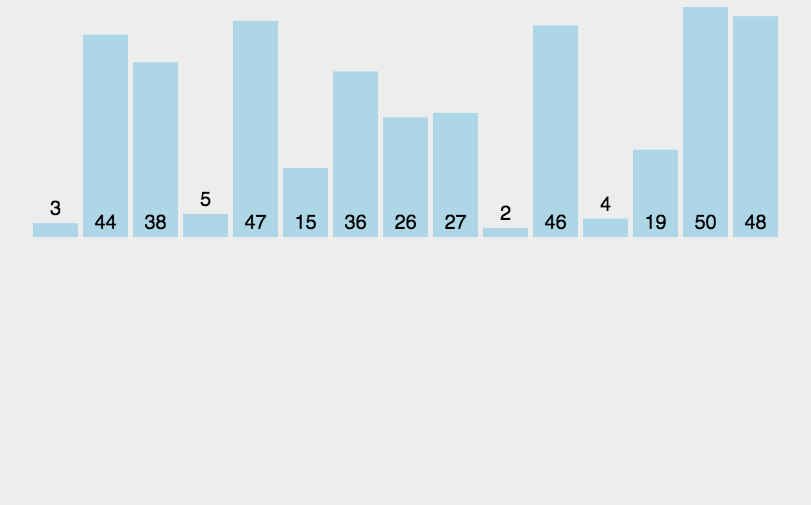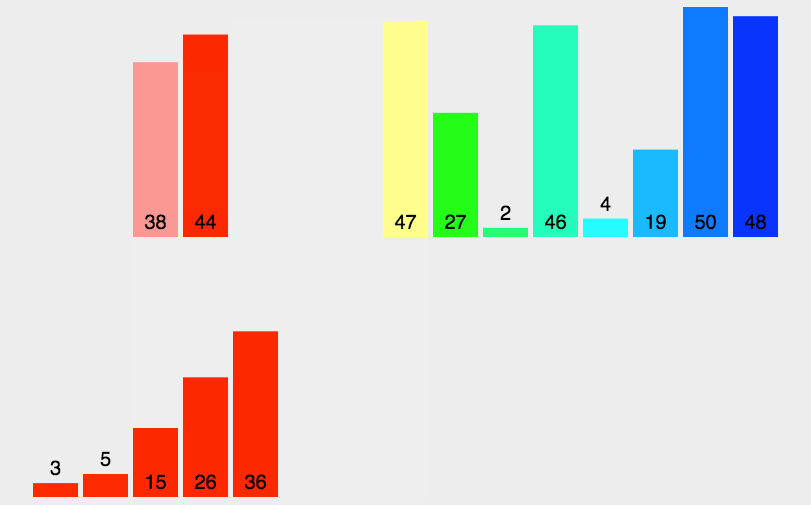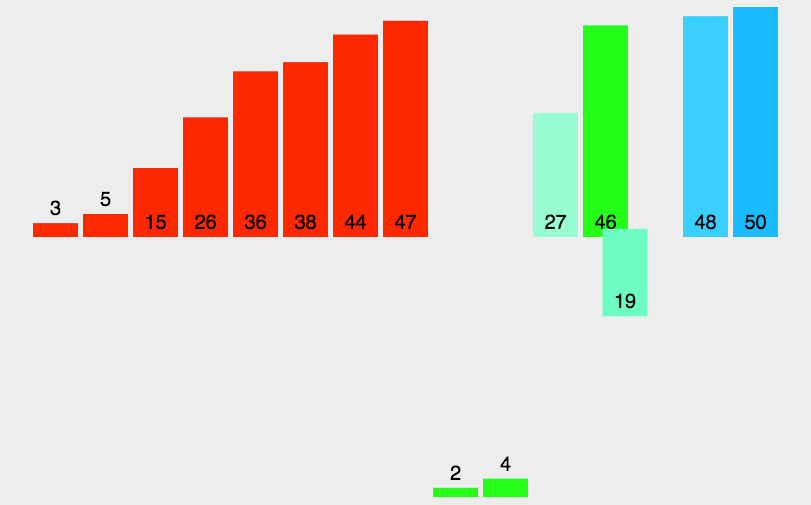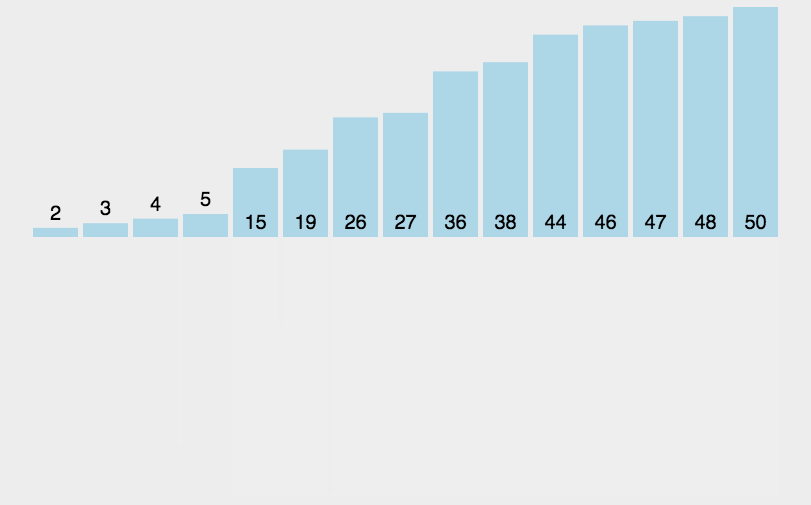
归并排序(Merge Sort)
- 把一个序列分成两半,先分别对每个子序列排序,然后再将两个子序列合并
- 一般采用递归法,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
1 | def merge_sort(A, a=0, b=None): |
基数排序(Radix Sort)
- 在Direct Access Array Sort、Counting Sort、Tuple Sort基础上演化出来的排序算法,将每个整数分解为n的幂次,根据幂级顺序进行元组排序,可以做到线性时间内完成排序
1 | def counting_sort(A): |