
定义:用来表示人、事物、地点以及抽象事物的名称
名词短语:名词与它的修饰词一起构成名词短语,用来修饰名词的词称为定语
- 组成规律:左二右六 - 限定词 + 形容词 + 中心名词 + 六类后置定语(介词短语、分词短语、不定式短语、形容词短语、定语从句、同位语从句)
1.1 名词的分类:
专有名词
表示特定的人、物、机构、场所的名词,首字母必须大写。如Pairs, the United State
- 1.人名与头衔,Winston Churchill, the Queen of the England, the Persident of the United States, Doctor Mathews, Professor Samuels
- 2.著作名称,War and Peace, Pride and Prejudice
- 3.月份,January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December
- 4.星期、四季,Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, winter, sunmer, spring, autumn
- 5.节日,Christmas, Easter, New Year’s Day
- 6.地理名称
- 国家及大洲的名称,America, Africa, Europe, Asia, England, Scotland, China, Peru, Albania
- 地区城市的名称,Rome, Vancouver, Beijing, Florence, California, Florida
- 江河湖的名称,the Atlantic, the Pacific, the Dead Sea, Lake Victoria, the Rhine, the Thames, the Nile
- 山脉、沙漠,the Himalayas, the Alps, the Sahara
普通名词
- 可数名词
- 个体名词:表示同类的人或物中的个体 。student,tree
- 集体名词:表示若干人或物的总称。team,committee
- 不可数名词
- 物质名词:表示物质和材料的的总称。paper,water
- 抽象名词:表示动作、性质、状态或情感等抽象名词。happiness,evolution,imagination
1.2 可数名词与不可数名词
五类不可数名词【U】
Group A - 无法分隔的物质名词
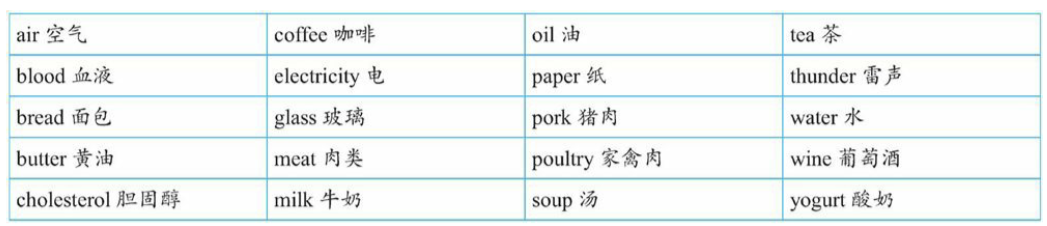
Group B - 组成成分较小的物质

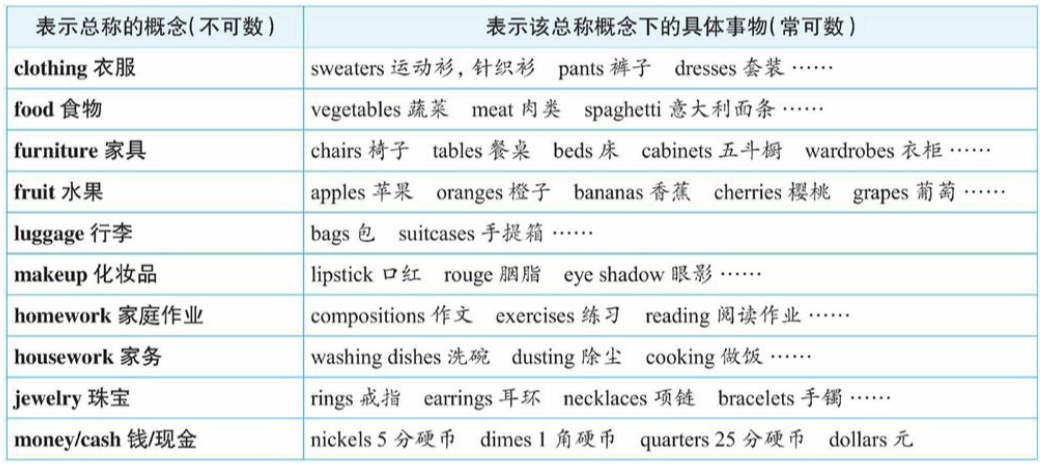
Group C - 表总称的名词(总称不可数,而总称概念下的具体事物是可数的)
一些容易混淆的总称名词
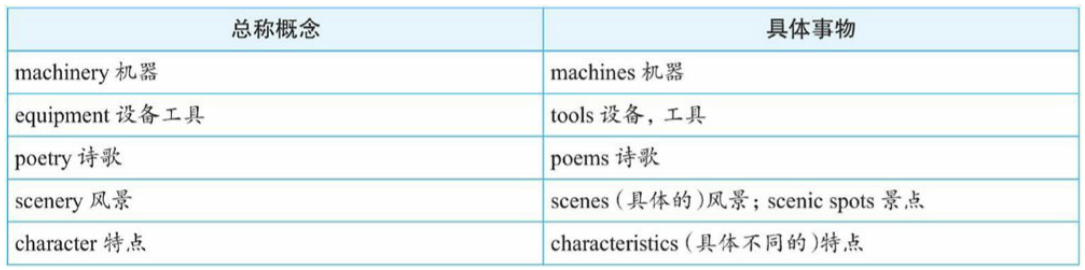
上面的左边一栏表示总称含义时,均为不可数名词,没有复数形式。
以character为例,当其表示总称时,含义为the combination of qualities or features that distinguish one person, group, or thing from others,如 a man of character ;
当其作为可数名词的时候,表示方块字,如a Chinese charater;
当要表示具体的、可数的特点的时候,需要用characteristics,如the socialism with Chinese characteristics.
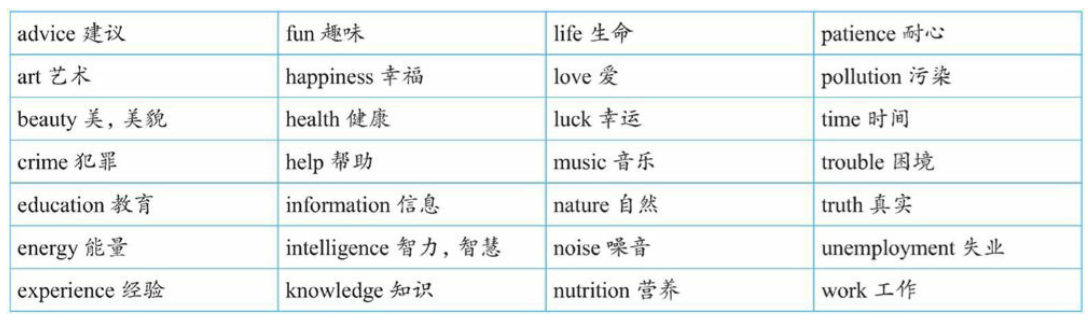
Group D - 抽象名词
Group E - 表示学科的词

可数不可数的相对论
一个名词是可数还是不可数关键在于它所表达的意思,而意义又随语境的不同而改变,因此名词的可数性是与它所使用的上下文语境密切相关的,不可数名词可能会可数化,可数名词可能会变为不可数名词。这种转变有如下几种规律:
- 规律一 - 物质名词或总称名词,若表示不同的种类,或有特定的意思,或是液体表示几杯、几瓶的数量,则可转化为不可数名词
- Would you like a cake? No, I don’t like cake.
- Two beers and three coffee, please.!
- He broke a glass.
- The waters of the Eat Sea.
- 规律二 - 对于抽象名词,具体化时可以转化为可数名词; 可数名词抽象化时可以变为不可数名词
- Knitting is an art.
- She was a beauty in her youth.
- There’s plenty of room for everyone to sit down in this room.
- I pronounce this couple to be husband and wife.
- 总结:总的来说,当一个名词表示抽象的、总称的概念时,一般作为不可数名词;而当表示具体的、特定的事物时,则通常作为可数名词
不可数名词的度量
不可数名词不能被a(an)修饰,不能被基数词修饰,但可以用量词来表示其量的概念:
- 常用piece来修饰一下的抽象名词和物质名词 - advice, bread, baggage, chalk, equipment, furniture, information, jewelry, luggage, music, news
- a piece of news
- several pieces of furniture
- 用bottle, cup, drop, glass修饰液态物质
- several drops of blood
- a glass of milk
- two cups of coffee
- 其他量词
- a loaf of bread
- a slice of meat
1.3 可数名词的单复数
名词的单复数
- 单数(sg.)与复数(pl.)
- 英文中对一以上的数量视为复数,如one half day, one and a half days,可数名词在复数下一般需要变换形式;当然英文也有双数的概念,如both, either, neither只能用来表示两者,不能用于两者以上的复数;each可以表示两者及以上,而every只能用于三者及以上,因此只能说each sex,不能说every sex。双数和三数与复数没有关系,因此我们把数分为单数、复数、单/复数。
- 只能用作单数的名词
- 英语中不可数名词和专有名词只能用作单数,没有复数形式,他们作主语时谓语动词要用单数第三人称形式。
- 只能用作复数的名词
- 二合一的复数名词 - 表示由相等的两部分联系在一起的工具、仪器或服装,描述数量时用pair修饰,用复数的代词代指
- glasses, binocular, scales, clipper, scissors, jeans, shorts, trousers
- a pair of glasses, a pair of pants
- Where are my glasses? They are right on your nose!
- 单行复义 - 形式上是单数,但表达复数的含义,往往也有单数的用法
- People - 作人民时,只有复数,作民族、部落时,有复数变化peoples
- Cattle - 作牛群只有复数
- Police - 通常表示警察部队、警方,为集体名词,个别、具体警官用a police officer, a policeman
- Poultry - 作家禽时只能用复数,作家禽的肉时要当作单数名词来用
- the + 形容词 - 表示一类人,作复数名词
- The rich are being richer.
- 复数专有名词
- the Alps, the Himalayas
- 二合一的复数名词 - 表示由相等的两部分联系在一起的工具、仪器或服装,描述数量时用pair修饰,用复数的代词代指
名词的复数化
- 规则的复数名词
- 一般名词在词尾加-s,book/books, hand/hands
- 以-s, x, -sh, -ch(发/k/时)结尾的名词加-es,classes, boxes, matches, bushes
- 以-o结尾的名词,有的加-s,有的加-es,tomatoes, heroes, kilos, pianos, photos, memos, bamboos, radios, studios, motto(e)s
- 辅音-y结尾的名词,变-y为-i加-es,原音+y结尾的名词直接加s,country/countries, baby/babies, plays, boys
- 以-f, -fe结尾的名词,有的变-v加-es,有的直接加-s,calf/calves, half/halves, life/lives, wife/wives, belifs, chiefs, safes, proofs
- 注意:beef(牛肉,不可数)/beefs(牢骚抱怨)/beeves(菜牛)
- 不规则的复数名词
- 以-a结尾的拉丁语名词,词尾变-ae或-as,formula/formulae/formulas
- 以-ex或-ix结尾的拉丁名词,在词尾直接加-es,或把-ex和-ix变为-ices,index/indexes/indices
- 以-is结尾的希腊语名词,变-is为-es,analysis/analyses, basis/bases, crisis/crises, diagnosis/diagnoses, thesis/theses
- 以-on或-um结尾的名词,变-on或-um为-a,有的可以直接加-s,criterion/criteria/criterions, datum/data, erratum/errata, medium/midia/mediums, phenomenon/phenomena
- 变-oo-为-ee-,foot/feet, tooth/teeth, goose/geese
- 变-ouse为-ice,mouse/mice, louse/lice
- 以-us结尾的拉丁语名词,变-us为-i,有的可以直接加-es,genius/genii/geniuses, nucleus/nuclei/nucleuses, stimulus/stimuli
- 复合名词变复数
- man/woman + 名词构成的复合名词,两个词需均变复数,man treacher/men teachers, woman journalist/women journalists
- 以-man/-woman/-child结尾的复合名词,将-man/-woman/-child变为复数,fireman/fireman, grandchild/grandchildren policeman/policemen
- 名词+介词/介词短语构成的符合名词,将主体名词变复数,passer-by/passers-by, comrade-in-arms/comrades-in-arms, looker-on/lookers-on
- 名词+形容词构成的复合名词,变名词为复数,Attorney General/Attoneys Gernal, consul general/consuls general
- 由短语动词演变的复合名词,直接在词尾加-s,forget-me-not/forget-me-nots, take-off/take-offs, stand-by/stand-bys, grown-up/grown-ups
- 单复数同形的名词
- 动物名词,sheep, deer, salmon, fish, flounder
- 国籍名词,Chinese, Japanese, British, Swiss
- 三类没有形式变化的名词
- 不可数名词,没有词形变化,只能用单数,如music
- 复数可数名词,没有词形变化,只能用复数,如people
- 单复数同形的名词,没有词形变化,但有单复数之分,如sheep
- 有新词义的复数名词
- arm(手臂)/arms(武器,军事), custom(风俗)/customs(海关), damage(损坏)/damages(赔偿金), letter(信)/letters(文学)
1.4 名词的所有格
‘s 所有格
- ‘s 所有格的构成:名词所有格’s主要用来表示有生命的名词的所属关系,通常用在姓名、人称、不定代词、集体名词和高等动物等名词的后面
- 单数名词,直接在词尾加’s,a woman’s intuition, the actress’s boyfriend
- 复数名词,不以-s或-es结尾的在词尾加’s,否则在词尾加’s,the Children’s Day, her friends’ money
- 复合名词,在最后一个词的词尾加’s,my father-in-law’s company, the Persident of America’s secretary
- 由and连接的并列名词,当表示共有含义时,在最后一个名词词尾加’s;当表示各自所有含义时,需在每个名词词尾加’s
- John and his wife’s bank savings. 约翰和他妻子的共有存款
- John’s and his wife’s bank savings. 约翰和他妻子各自的存款
- ‘s所有格的逻辑关系
- 所属关系,某人拥有某物,或某物属于某一类人,my sister’s boyfriend, women’s wear
- 主谓关系,the visitor’s departure = the visitor departed, Britain’s decision = Britain decided
- 动宾关系,the children’s education = educated the children, the boy’s punishment = punishd the boy
- 同位关系,Bhutoo’s loss
- 表时间或距离,tomorrow’s weather, a month’s salary, three hours’ delay,
- 表度量,two pounds’ weight, ten dollars’ worth of meat
- ‘s所有格修饰的名词被省略
- 避免名词重复:若名词所有格所修饰的名词已经出现过,则第二次出现的所有格后面的名词可被省略,This bike is mine, not Mahael’s.
- 表示店铺或教堂,一般要在所有格名词前面加the,at the chemist’s = at the chemist’s shop
- 表示某人的住宅,人名后的所有格省略名词,表示某人的住宅,go to my sister’s = go to my sister’s home
of 属格
- of 属格的构成:N1+of+N2,一般表示无生命物体名词的所有关系,或有生命名词后接短语或从句修饰的属格(定语后置,方便修饰)
- 表示无生命物体名词的所有关系,The name of the song.
- 有生命名词后接短语或从句修饰的属格,What’s the name of the boy sitting next to her?
of属格的逻辑关系(常用)
- 主谓关系,从右向左翻译,the arrival of the train, the growth of agriculture
动宾关系,从左向右翻译,Americia’s invasion of Iraq, a statement of face, the disicission of the plan
对于及物动词一般按动宾关系理解,不及物动词一般主谓关系理解,而既及物又不及物的动词会出现问题 - the shooting of the rebels
同位关系,两者互为同位说明,the city of Rome, the news of the team’s victory